Coaching for Success
Introducing eFIRE
Now you’ve had a chance to think about coaching, and its differences to other forms of WIL partner – student interaction, it’s time to identify how to engage in a coaching conversation. This topic presents a coaching model that can be applied to practically any WIL context, including teams. It includes examples of questions that can be asked to help students:
- better understand the problems they are facing
- identify realistic strategies to solve them
- experiment with available options and develop action plans that consider the impacts of their execution.
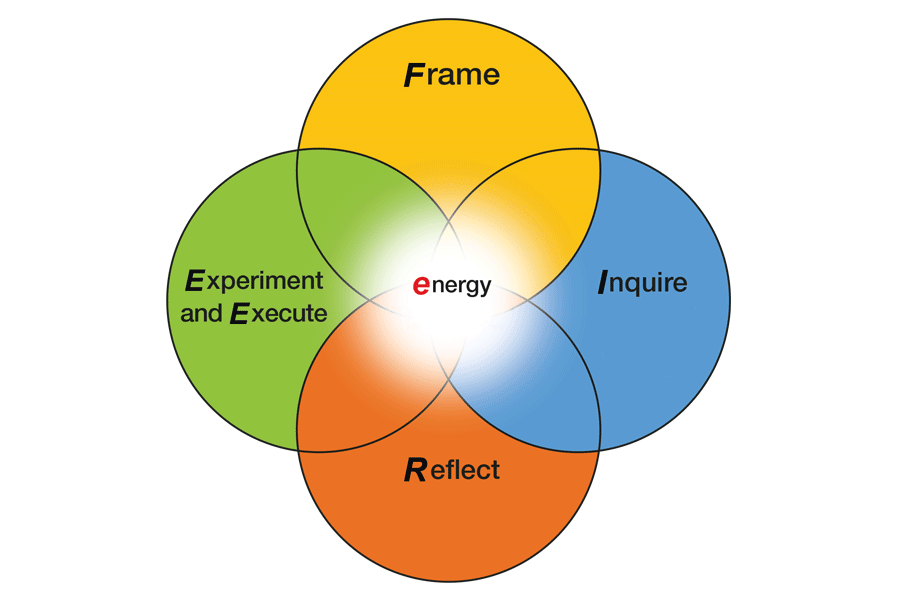
Coaching, in practice, is essentially a formal conversation framework that helps a coach support the development of the coachee. In the context of Work Integrated Learning (WIL) relationships, a WIL partner would be considered the coach, and the student(s) would be considered the coachee. The coaching model introduced in this module is called eFIRE. eFIRE is described as a non-linear model of coaching that is designed to enable conversations to go beyond surface-level issues (Abbott, 2016) to activate changes in behaviour, in line with Boyatzis’ (2006) Intentional Change Theory. The eFIRE model consists of five distinct modes of conversation:
- energy
- Framing
- Inquiring
- Reflecting
- Executing/Experimenting